In the world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, transactions are the lifeblood of the decentralized ecosystem. Whether you’re sending Bitcoin, Ethereum, or any other digital asset, each transaction leaves a unique digital fingerprint known as a transaction hash. This seemingly complex alphanumeric string plays a crucial role in ensuring the security, transparency, and immutability of blockchain transactions. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of transaction hashes, exploring their significance and how they contribute to the reliability of blockchain networks.
What is a Transaction Hash?
A transaction hash, often referred to as a transaction ID or TXID, is a cryptographic hash function generated from the details of a blockchain transaction. It serves as a unique identifier for each transaction, allowing participants on the blockchain network to trace and verify the details of a specific transaction. This hash is typically a fixed-length alphanumeric string, ensuring its uniqueness and making it practically impossible to alter or counterfeit.
Structure of a Transaction Hash
A transaction hash is generated by applying a cryptographic hash function, such as SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit), to the transaction data. This data includes information such as:
- Sender’s Address: The public key or address of the party initiating the transaction.
- Recipient’s Address: The public key or address of the recipient.
- Amount Transferred: The quantity of cryptocurrency being sent.
- Transaction Timestamp: The time at which the transaction was initiated.
- Transaction Fee: The fee paid by the sender for transaction processing.
The combination of these elements, when subjected to the cryptographic hash function, produces the unique transaction hash.
Importance of Transaction Hashes
- Verification and Immutability: Transaction hashes play a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and immutability of blockchain transactions. Participants can verify the authenticity of a transaction by comparing its hash with the recorded information on the blockchain.
- Traceability: Transaction hashes enable users to trace the journey of funds through the blockchain. By examining the transaction history associated with a particular hash, participants can gain insights into the flow of digital assets.
- Security: Cryptographic hash functions provide a high level of security. Even a small change in the transaction data results in a significantly different hash, making it nearly impossible for malicious actors to tamper with transactions unnoticed.
Locating Transaction Hashes
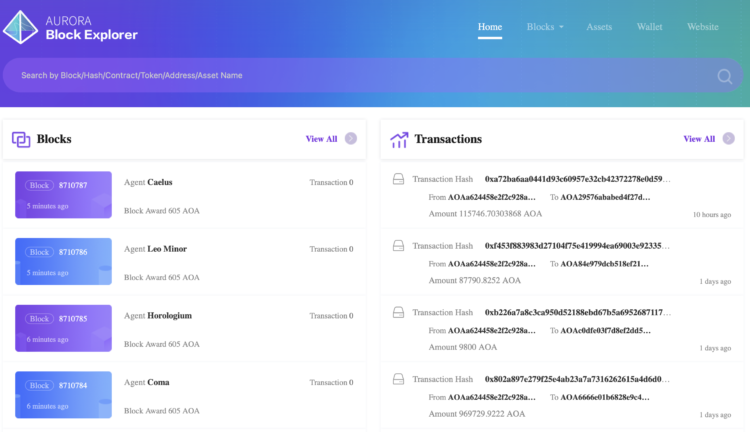
Transaction hashes are typically accessible through blockchain explorers – web-based tools that allow users to inspect and track transactions on a blockchain. Users can input the transaction hash into a blockchain explorer to access detailed information about the transaction, including its status, confirmation time, and associated addresses.
Summary
In the dynamic world of blockchain, transaction hashes serve as the backbone of trust and transparency. Their unique and unalterable nature ensures that participants can rely on the integrity of transactions, fostering a secure and efficient decentralized ecosystem. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, understanding the significance of transaction hashes becomes increasingly crucial for anyone engaging in cryptocurrency transactions.